Arcana#
Arcana (Abstraction of Repository-Centric ANAlysis) is an informatics framework for analysing datasets “in-place”, i.e. pulling data from a data store to a (typically neighbouring) computing resource, performing computations on the data, and then uploading the processed data back to the store alongside the original data. Arcana has been designed to address many of the challenges typically faced when analysing large medical-imaging projects, but should make your life easier no matter the size of your dataset or field of study!
Data store interactions are abstracted by modular handlers, making worklows portable between different storage systems. Other tedious aspects of workflow design, such as iteration, file-format conversions and management of provenance data are also abstracted away from the designer, enabling them to focus on the core logic of the analysis to be implemented.
Arcana’s approach has several advantages over typical workflow design, particularly when analysing large datasets:
Derivatives are kept in central location, avoiding duplication of processing
Incremental processing facilitates manual-QC of intermediate products at key milestones in the workflow (e.g. brain masks)
Abstraction of implementation details promotes development of shared workflow libraries, which can be refined over time to capture the domain-specific arcana of data analysis (the obscure knowledge required to apply an appropriate combination of tools and parameters to analyse complex datasets).
The Arcana framework can be broken down into four conceptual layers:
Core layer - abstract base classes and core pipeline logic
Infrastructure layer - Repository system connectors, file formats and data structures
Processing layer - Preprocessing pipelines and methods to derive standard markers
Analysis layer - Statistical analysis methods and study-specific customisations
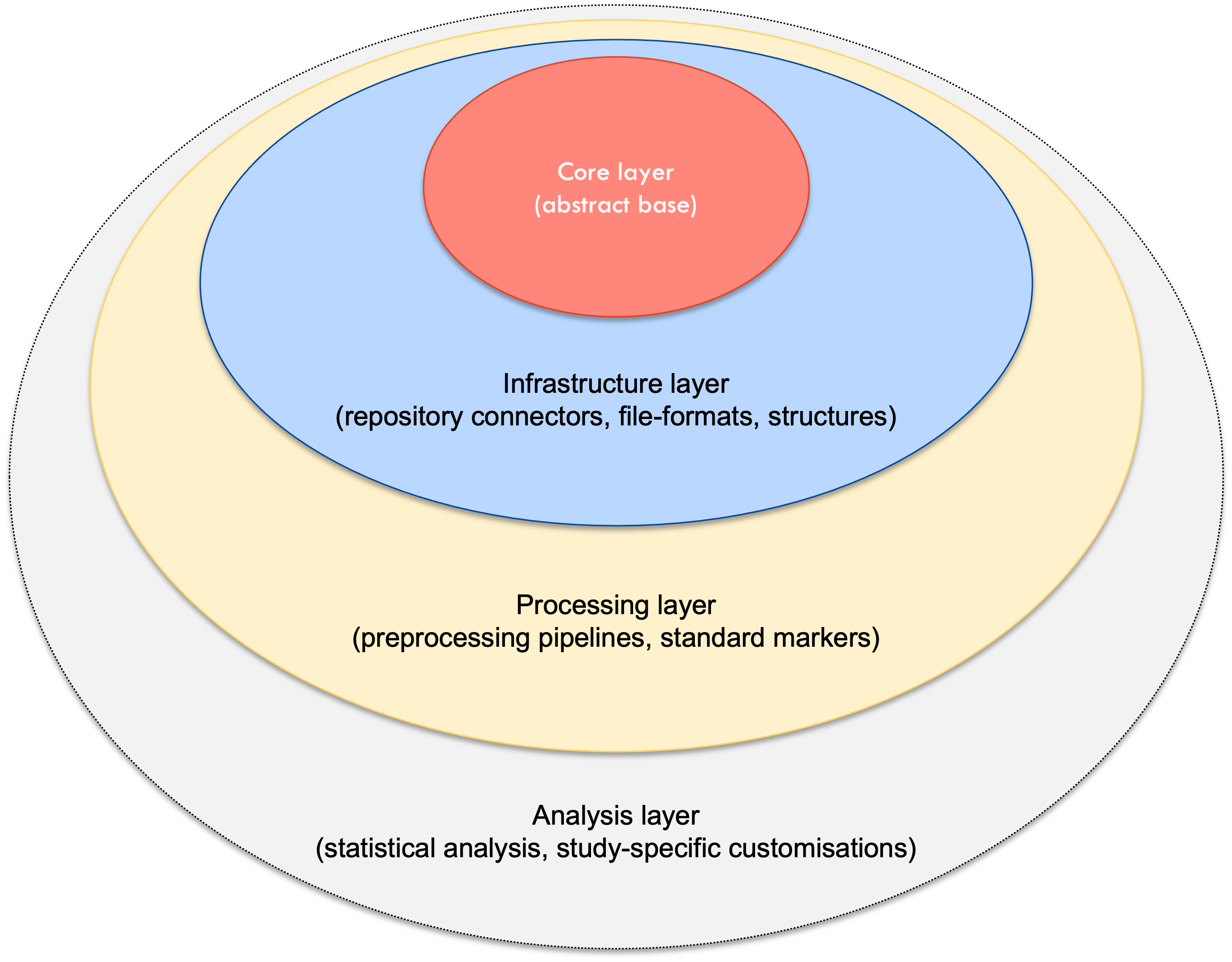
The core and infrastructure layers are largely developed by the main Arcana developer team (see Authors). Processing layers for neuro-MRI and molecular imaging are being developed as part of the Australian Imaging Service in the core pipelines repository. Since the analysis layer is typically study-specific, it is often left to the end user to implement (noting that outputs from the processing layer can be used directly if desired)
Although designed to efficiently handle the requirements typical of medical imaging workflows (i.e. manipulation of file-based images by various third-party tools), at its core, Arcana is a general framework, which could be used to design analyses in any field. If you do end up using Arcana in a different domain please post an issue about it in the issue tracker to let us know!
Arcana also includes tools for deploying pipelines in Docker images that can be run in XNAT’s container service (BIDS apps support is planned in the future) . These tools can be used to maintain continuous integration and deployment of pipeline suites (see Australian Imaging Service Pipelines).
Note
For the legacy version of Arcana as described in Close TG, et. al. Neuroinformatics. 2020 18(1):109-129. doi: 10.1007/s12021-019-09430-1 please see https://github.com/MonashBI/arcana-legacy. Conceptually, the legacy version and the versions in this repository (version >= 2.0) are similar. However, instead of Nipype, versions >= 2 use the Pydra workflow engine (Nipype’s successor) and the syntax has been rewritten from scratch to make it more streamlined and intuitive.